Introduction
Nginx is one of the most popular web servers in the world and currently it is considered a web-server of greater flexibility, resource and is responsible for hosting some of the largest and highest-traffic sites.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, you should have a regular, non-root user with sudo privileges configured on your server.
Step 1 - Installing Nginx
Nginx is available in Ubuntu's default repositories, it is possible to install it from these repositories using the apt packaging system.
Since this is our first interaction with the apt packaging system in this instance, we will update our local package index so that we have access to the most recent package listings. Afterwards, we can install nginx:
$$sudo apt update
sudo apt install nginx -y (-y means automatic yes)
After accepting the procedure (automatic), apt will install Nginx and any required dependencies to your server.
Step 2 - Adjusting the Firewall
Before testing Nginx, the firewall software (ufw) needs to be adjusted to allow access to the service.
List the application configurations that ufw knows how to work with by typing:
$sudo ufw app list
You should get a listing of the available applications profiles:
Nginx Full
Nginx HTTP
Nginx HTTPS
OpenSSH
As you can see, there are three profiles available for Nginx:
- Nginx Full: This profile opens both port 80 (normal, unencrypted web traffic) and port 443 (TLS/SSL encrypted traffic)
- Nginx HTTP: This profile opens only port 80 (normal, unencrypted web traffic)
- Nginx HTTPS: This profile opens only port 443 (TLS/SSL encrypted traffic)
It is recommended that you enable both ports (Nginx Full) because after this guide, it is highly recommended that you install the Lets Encrypt (port 443) on your Nginx.
You can enable this by typing:
$sudo ufw allow 'Nginx HTTPS'
You can verify the change by typing:
$sudo ufw status
You should see HTTP and HTTPS traffic allowed in the displayed output:
Status: activeTo Action From
OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere Nginx HTTP ALLOW Anywhere OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) Nginx HTTPS (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Step 3 – Checking your Web Server
At the end of the installation process, Ubuntu 18.04 starts Nginx. The web server should already be up and running. We can check with the systemd init system to make sure the service is running by typing:
$systemctl status nginx
● nginx.service - A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: <span class="text-success">active (running)</span> since Fri 2018-04-20 16:08:19 UTC; 3 days ago
Docs: man:nginx(8)
Main PID: 2369 (nginx)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 1153)
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
├─2369 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on;
└─2380 nginx: worker process
As you can see above, the service appears to have started successfully. However, the best way to test this is to actually request a page from Nginx.
You can access the default Nginx landing page to confirm that the software is running properly by navigating to your server's IP address. If you do not know your server's IP address, you can get it a few different ways.
Try typing this at your server's command prompt:
$ip addr show eth0 | grep inet | awk '{ print $2; }' | sed 's//.*$//'
You will get back a few lines. You can try each in your web browser to see if they work.
An alternative is typing this, which should give you your public IP address as seen from another location on the internet:
$curl -4 ifconfig.me
When you have your server's IP address, enter it into your browser's address bar:
http://your_server_ip
You should see the default Nginx landing page:
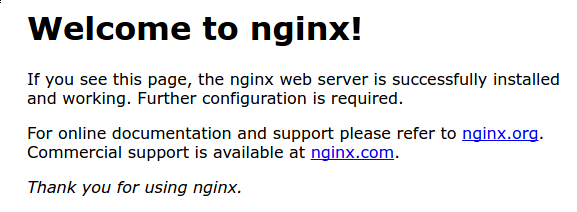 This page is included with Nginx to show you that the server is running correctly.
This page is included with Nginx to show you that the server is running correctly.
Step 4 - Managing the Nginx Proces
Now that you have your web server up and running, let's review some basic management commands.
To stop your web server, type:
$sudo systemctl stop nginx
To start the web server when it is stopped, type:
$sudo systemctl start nginx
To stop and then start the service again, type:
$sudo systemctl restart nginx
If you are simply making configuration changes, Nginx can often reload without dropping connections. To do this, type:
$sudo systemctl reload nginx
By default, Nginx is configured to start automatically when the server boots. If this is not what you want, you can disable this behavior by typing:
$sudo systemctl disable nginx
To re-enable the service to start up at boot, you can type:
$sudo systemctl enable nginx
Step 5 - Setting Up Server Blocks (Recommended)
When using the Nginx web server, server blocks (similar to virtual hosts in Apache ) can be used to encapsulate configuration details and host more than one domain from a single server. We will set up a domain called: 'yoursite.com', but you should replace this with your own domain name.
Nginx on Ubuntu 18.04 has one server block enabled by default that is configured to serve documents out of a directory at var/www/html. While this works well for a single site, it can become unwieldy if you are hosting multiple sites. Instead of modifying /var/www/html, let's create a directory structure within /var/www for our 'yoursite.com' site, leaving /var/www/htm in place as the default directory to be served if a client request doesn't match any other sites.
Create the directory for 'yoursite.com' as follows, using the -p flag to create any necessary parent directories:
$sudo mkdir -p /var/www/yoursite.com/html
Next, assign ownership of the directory with the $USER environment variable:
$sudo chown -R $USER:$USER /var/www/yoursite.com/html
The permissions of your web roots should be correct if you haven't modified your umask value, but you can make sure by typing:
$sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/yoursite.com
Next, create a sample index.html page using nano or your favorite editor:
$sudo nano /var/www/yoursite.com/html/index.html
Inside, add the following sample HTML:
index.html
<title>Welcome to YourSite.com
Success! The yoursite.com server block is working!
Save and close the file when you are finished.
In order for Nginx to serve this content, it's necessary to create a server block with the correct directives. Instead of modifying the default configuration file directly, let’s make a new one at /etc/nginx/sites-available/yoursite.com:
$sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/yoursite.com
Paste in the following configuration block, which is similar to the default, but updated for our new directory and domain name:
/etc/nginx/sites-available/yoursite.com
server { listen 80; listen [::]:80; root /var/www/yoursite.com/html; index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html;
server_name example.com yoursite.com;
location / { try_files $uri $uri/ =404; } }
Notice that we’ve updated the root configuration to our new directory, and the server_name to our domain name.
Next, let's enable the file by creating a link from it to the sites-enabled directory, which Nginx reads from during startup:
$ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/yoursite.com/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
Two server blocks are now enabled and configured to respond to requests based on their listen and server_name directives (you can read more about how Nginx processes these directives here):
yoursite.comWill respond to requests for yoursite.com and www.yoursite.com.- default: Will respond to any requests on port 80 that do not match the other two blocks.
To avoid a possible hash bucket memory problem that can arise from adding additional server names, it is necessary to adjust a single value in the etc/nginx/nginx.conf file. Open the file:
$sudo nano /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
Find the server_names_hash_bucket_size directive and remove the # symbol to uncomment the line:
/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
... http { ... server_names_hash_bucket_size 64; ... } ...
Next, test to make sure that there are no syntax errors in any of your Nginx files:
$sudo nginx -t
Save and close the file when you are finished.
If there aren't any problems, restart Nginx to enable your changes:
$sudo systemctl restart nginx
Nginx should now be serving your domain name. You can test this by navigating to http://yoursite.com, where you should see something like this:
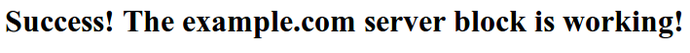
Step 6 - Getting Familiar with Important Nginx Files and Directories
Now that you know how to manage the Nginx service itself, you should take a few minutes to familiarize yourself with a few important directories and files.
Content
var/www/htmlThe actual web content, which by default only consists of the default Nginx page you saw earlier, is served out of the/var/www/htmldirectory. This can be changed by altering Nginx configuration files.
Server Configuration
/etc/nginx:The Nginx configuration directory. All of the Nginx configuration files reside here./etc/nginx/nginx.conf:The main Nginx configuration file. This can be modified to make changes to the Nginx global configuration./etc/nginx/sites-available:The directory where per-site server blocks can be stored. Nginx will not use the configuration files found in this directory unless they are linked to the sites-enabled directory. Typically, all server block configuration is done in this directory, and then enabled by linking to the other directory./etc/nginx/sites-enabled:The directory where enabled per-site server blocks are stored. Typically, these are created by linking to configuration files found in the sites-available directory./etc/nginx/snippets: This directory contains configuration fragments that can be included elsewhere in the Nginx configuration. Potentially repeatable configuration segments are good candidates for refactoring into snippets. Server Logs/var/log/nginx/access.log: Every request to your web server is recorded in this log file unless Nginx is configured to do otherwise./var/log/nginx/error.log: Any Nginx errors will be recorded in this log.
Conclusion
Now that you have your web server installed, you have many options for the type of content to serve and the technologies you want to use to create a best experience.







0 COMMENTS